The Port Authority of Valencia (PAV) has approved the award to Valencian company Baleària Eurolineas Marítimas S.A. for the construction and operation of the new public passenger terminal worth about $102 million (€100 million). According to the PAV, the maritime station will operate with zero polluting emissions and will be committed to the circular economy. The new passenger terminal will guarantee that 100% of the necessary electrical energy will be produced in the facilities themselves and will be of renewable origin: photovoltaic, wind, renewable hydrogen, or biofuel.
Major UK port opts for shore power for tugs to cut CO2 footprint: Portsmouth International Port has ambitious targets to reach net zero by 2030 and become emission-free by 2050. The port is also working closely with all its partners to enable them to reach their sustainability goals. With the new shore power project, the port estimates that 131 tons of carbon per annum will be saved.

Green corridors
New green corridors hub launched to accelerate shipping decarbonization: Zero-Emission Shipping Mission, which aims to accelerate international collaboration to scale and deploy new green maritime solutions, has launched ‘The Green Shipping Corridors Hub’ to support action to realize green shipping corridors.
The hub, launched at COP27, forms part of the Blueprint for Future Ports Program published in September as part of the Mission Action Plan at the Global Clean Energy Action Forum in Pittsburgh. The tools, documents, and other resources on the hub platform are provided by the members of the Shipping Mission to help accelerate the maritime energy transition. The launch is a call to all industry members to engage with the tools on the platform. The program aims to create a blueprint for what a zero-emission fuel-ready port will look like in 2030.
Governments
Singapore is to invest an additional SGD129m in low-carbon energy research in 2022 to support critical enablers of Singapore’s energy transition: Low Yen Ling, Minister of State, Ministry of Culture, Community and Youth & Ministry of Trade and Industry opened OSEA (Offshore Southeast Asia) 2022 and welcomed delegates from more than 60 countries, highlighting the importance of investment in research and innovation. In line with Low’s speech, Singapore will invest SGD129m in low-carbon energy research (LCER) in 2022, significant amounts in projects to help import, handle, and utilize hydrogen safely and at scale. This investment adds to SGD55m already awarded to LCER projects.
Regulations
Bimco adopts CII clause: The clause starts from the position that the charterer should take responsibility for CII as the decision maker for ship operations which will impact the vessel's CII rating. CII regulations enter into force in January 2023 and will rate vessels based on their CO2 emissions per cargo capacity per nautical mile traveled. The regulation is expected to dramatically impact vessel deployments and operations as owners and operators look to attain and maintain certain CII ratings.
 EU boosts IMO’s energy-efficiency project with additional €10mln investment:
EU boosts IMO’s energy-efficiency project with additional €10mln investment: The European Commission has revealed it will invest an additional €10 million for an energy-efficiency project to reduce international shipping’s greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions through a global network of Maritime Technology Cooperation Centres (MTCCs), which is managed by the International Maritime Organisation (IMO). The project, funded by the European Union (EU), began work in 2016, establishing five regional MTCCs around the world. The centers promoted energy efficiency through national and regional capacity-building seminars, as well as demonstration projects (in Shanghai, Nairobi, Fiji, Trinidad and Tobago and Panama). The projects involved port energy-efficiency assessments, equipping port vessels with solar power, and establishing data collection systems for ship GHG emissions. The new funding makes possible a second phase of the project, focusing on portside energy efficiency measures.
By Maria Bertzeletou, Breakwave Advisors
The opinions expressed herein are the author's and not necessarily those of The Xinde Marine News.
Please Contact Us at:
media@xindemarine.com
















 Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar 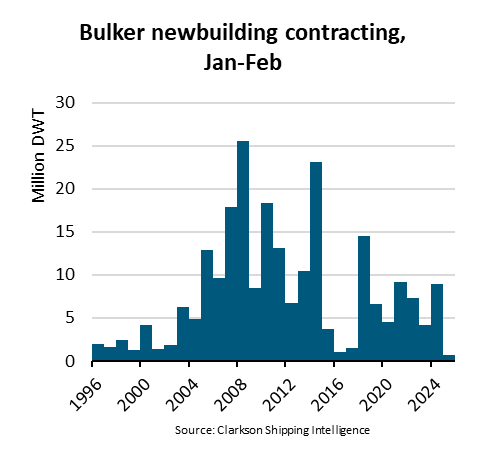 BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi
BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar