Other major shipping companies including Maersk and recently CMA CGA have followed suit also ordering methanol-fueled containerships while others are also adopting dual-fuel technologies capable of future methanol operation. One of the key questions, however, has been the availability and supply of methanol especially to meet the near-term needs of the shipping industry. Stena Proman however points out that methanol is already available at over 100 ports worldwide, including at all major bunkering hubs. They are confident that methanol will become a key part of the environmental transition for the shipping industry.
Brazilian state-owned oil and gas giant Petrobras has welcomed the arrival of the first of three purpose-built, Suezmax second-generation dynamic positioning (DP2) shuttle tankers, which will carry out operations offshore Brazil. The other two are expected to join the energy player's eco-type fleet by the end of 2022. Petrobras disclosed that it has been investing in the contracting of sustainable ships, known as eco-type, which already represent around 37 percent of the fleet of ships contracted by the company. The Brazilian firm says that these vessels were built from 2015 onwards to comply with the energy efficiency improvement measures established by the International Maritime Organization (IMO/IMO), which aim to reduce fuel consumption and gas emissions in the atmosphere.
Maritime classification society Lloyd's Register (LR) has granted an approval in principle (AiP) for K Shipbuilding's design of a 7,700 TEU liquefied natural gas (LNG)-powered containership. The AiP certification is a procedure to verify the suitability of the ship's basic design. In order to minimize the loss of space in the existing containership design, the South Korean shipbuilder put the living area in the front, as part of the ship's design, and an LNG storage tank of about 6,800 cbm was placed below it.
SeaShuttle, the ambitious project to build two hydrogen-powered, remotely controlled and autonomous-ready containerships, has secured NOK 150 million (€15 million) in funding from Norwegian state enterprise Enova. The bold scheme, led by Dutch multimodal transport and logistics group Samskip and the U.S.-based marine robotics specialist Ocean Infinity, envisages two SeaShuttle ships operating emissions-free between Oslo Fjord and Rotterdam, with each powered by a 3.2MW hydrogen fuel cell. The funding means the partners can move forward to contract the two new 500 TEU ships installed with the main propulsion solution that can be adapted to run on hydrogen fuel. A diesel-electric propulsion plant will be on board as a backup.
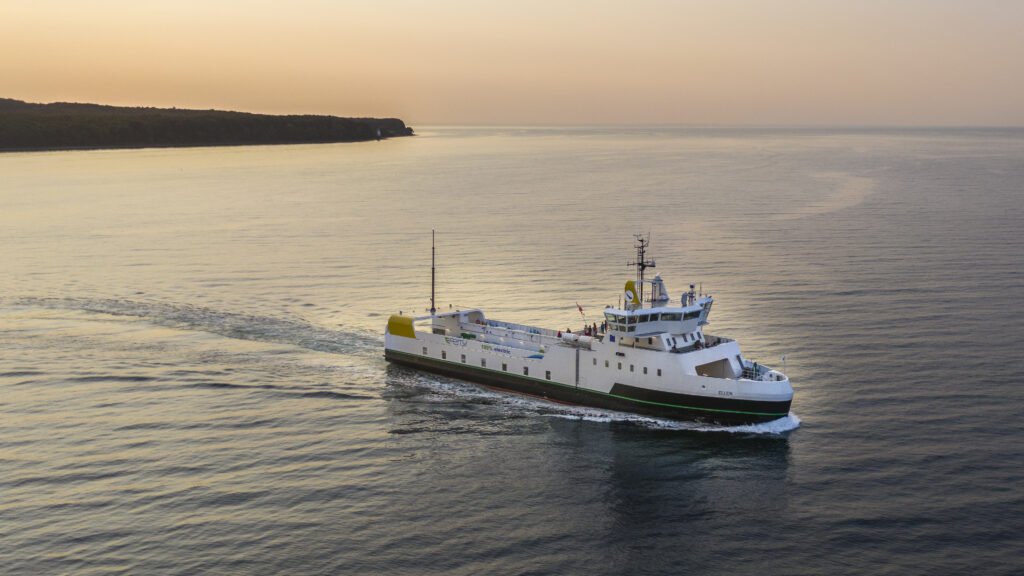
An all-electric ferry sails 90 km on a single battery charge, setting a world record: Ellen, the world's longest-ranging fully electric ferry, set a new world record on 9 June in Sønderborg, Denmark, during the International Energy Agency (IEA) 7th Annual Global Conference on Energy Efficiency. On its return from the conference, Ellen sailed 50 nautical miles – 92 kilometers – on a single battery charge. This is the longest recorded distance for an electric ferry able to carry passengers and vehicles to date anywhere in the world, according to the Danish engineering company Danfoss.
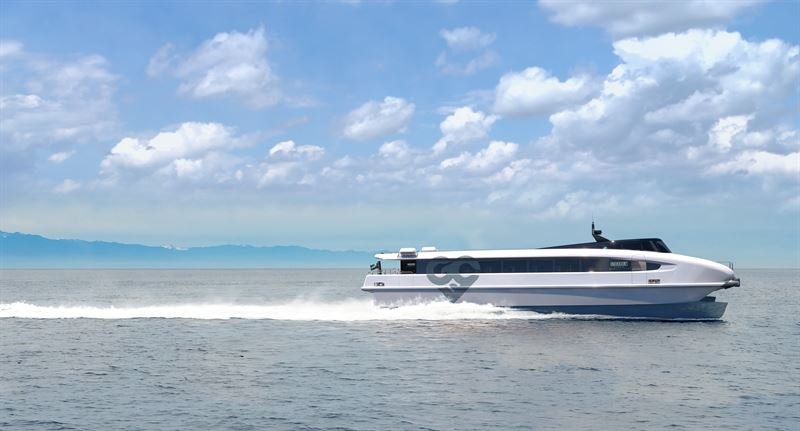
 Swedish energy systems provider Echandia picked for 2nd emission-free catamaran in Stockholm:
Swedish energy systems provider Echandia picked for 2nd emission-free catamaran in Stockholm: The Swedish energy systems provider Echandia has received a second order from compatriot company Green City Ferries AB. The Beluga24 is the world's first fully emission-free, high-speed, carbon fiber catamaran, and Echandia has been chosen to provide energy solutions for the vessels. The order is worth approximately SEK 7.5 million (EUR 702 thousand). Late last year, Echandia announced its first order for a fuel cell energy solution to power the first Beluga24 vessel from Green City Ferries.
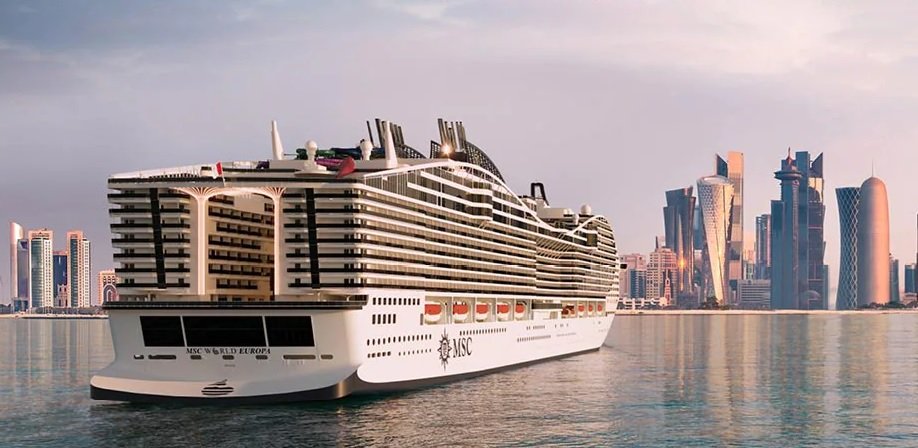
 MSC Cruises' LNG newbuilds mark construction milestones:
MSC Cruises' LNG newbuilds mark construction milestones: The cruise division of MSC Group, MSC Cruises, has marked two important milestones for the first two liquefied natural gas (LNG) vessels under construction in Chantiers de l'Atlantique's shipyard in Saint-Nazaire, France. MSC World Europa, the first LNG vessel to join the cruise line's fleet and set to become the biggest LNG-powered cruise ship in the world, completed its first set of sea trials in the Atlantic Ocean. The trials included testing the performance of the ship's engines, manoeuvrability, fuel consumption, safety systems, speed, and stopping distances.
 Wärtsilä and Stena to build the world's largest hybrid vessels:
Wärtsilä and Stena to build the world's largest hybrid vessels: The technology group Wärtsilä will supply its hybrid propulsion system for three new RoPax vessel currently built for Stena RoRo, Europe´s largest ferry company. Two of the ferries will have a battery capacity of 11.5 MWh, making them the marine industry's largest hybrid vessels to date. This battery power is approximately double that typically being used currently for hybrid propulsion. The order was placed in May 2022.

Shipyards
Kawasaki Heavy wins LPG/ammonia carrier order: Japanese shipowner Kumiai Navigation has ordered a liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) and liquefied ammonia gas (NH3) carrier powered by LPG fuel from compatriot shipbuilder Kawasaki Heavy Industries (KHI). The vessel will have a capacity of 86,700 cbm. It has separate cargo tanks designed to carry LPG and ammonia at the same time. Moreover, this is the first LPG/ammonia carrier for Kumiai. This contract represents the 77th LPG carrier, 14th LPG-fueled LPG carrier, and seventh LPG/ammonia carrier to be constructed by Kawasaki. Kawasaki plans to complete the construction of the vessels at its Sakaide Works in 2025.
Fincantieri cuts steel for TUI Cruises' 1st LNG-powered cruise ship: Italian shipbuilding company Fincantieri has held a steel cutting ceremony for the first of two new liquefied natural gas (LNG)-powered cruise ships for TUI Cruises, a joint venture between TUI AG and Royal Caribbean Cruises. The steel-cutting ceremony was held on 22 June in San Giorgio di Nogaro (Udine) at Centro Servizi Navali, a company that specialized in logistics and production of sheet metal for the Fincantieri yards located in northeastern Italy. The new ships, described as being the “backbone” of the future TUI Cruises' fleet, will have about 160,000 gross tons and will be able to operate on LNG as a fuel. Furthermore, the Italian shipbuilder is exploring possibilities to make them operate in the future with low-emission biofuels.

Fuels
ESL Shipping to start using revolutionary low-emission fuel: Finnish shipping company ESL Shipping will become the world's first shipping company to start utilizing new low-emission Neste Marine 0.1 co-processed marine fuel in its vessels in Finland and Sweden. The ISCC PLUS certified marine fuel enables up to 80% reduced greenhouse gas emissions over the life cycle compared to fossil fuels, the fuel's developer claims. Neste Marine 0.1 co-processed marine fuel is currently in the piloting phase and it is produced at Neste's refinery in Porvoo, Finland, where part of the fossil raw materials have been replaced with renewable raw materials in the conventional refining process. The drop-in fuel can be taken into use without any fleet modifications as it has a similar composition to conventional bunker fuels.

ZeroNorth unveils a new Vessel Selection service for fuel consumption estimates: The Technology company has unveiled its new Vessel Selection decision-making support service for charterers, which is powered by industry-leading analytics and data within the ZeroNorth Platform. The new service enables charterers to improve fuel consumption predictions by simulating various operating conditions for the vessels they are considering chartering. They can then select the right vessel for the specific route and conditions and negotiate more precise performance guarantees with owners to reduce the likelihood of cost overruns.
Shipfinance
Swiss charterers and shipping firms beat UK rivals to green trade finance: More than half (54%) of Switzerland-based carriers, forwarders and charters obtain preferential green trade finance by demonstrating compliance with banks' carbon and sustainability requirements, compared with 46% in UK, revealed new research by Pole Star, the global leader in vessel-tracking and sanctions screening for maritime and risk intelligence.

Ports
Georgia Ports Authority is a new member of Green Marine: The top U.S. container port by loaded export volume is the newest participant in Green Marine, a voluntary environmental certification program for North America's maritime industry. Operating the deepwater ports of Savannah and Brunswick along with two inland terminals, GPA is active on various fronts when it comes to sustainable development, winning an EPA Clean Air Excellence Award for its efforts.

Ports of Rotterdam, Baie-Comeau to collaborate on port development: The ports have agreed to execute a master plan study including cargo flow analyses and technical port infrastructure assessments. The study will also include an analysis of the production and use of the potential of green energy in the industrial zone, such as wind and solar power, bioenergy, and green hydrogen.

Long Beach City Council OKs resolution calling for 100% zero-emissions shipping: Long Beach City Councilmember Cindy Allen introduced the resolution on Earth Day, 22 April, calling on Long Beach's top maritime importers to commit to making all port calls to the San Pedro Port Complex, which includes the Port of Long Beach, on 100% zero-emissions ships by 2030. This resolution unites the U.S. largest ports, Los Angeles and Long Beach – and the largest U.S. seaport complex – in making the commitment of zero-emissions ocean shipping by 2030. It also calls on the Port of Long Beach to establish more green international ocean shipping corridors, building off the recently announced Shanghai to Los Angeles and Long Beach corridor.

Regulations
NGOs and industry leaders call for minimum H2 standard in FuelEU regs: Viking Cruises, Transport & Environment, Siemens, and other leading maritime businesses and NGOs have called on the EU to require a minimum share of hydrogen in the industry's fuel mix by 2030. The proposal would modify the EU's proposed FuelEU Maritime alternative-fuel plan by adding a "dedicated e-fuels sub quota" equivalent to six percent sustainable and scalable hydrogen. The group also called for targets for the construction of hydrogen-based fuel bunkering infrastructure in European ports to ensure availability.
The dozens of signatories to the proposal include prominent players in maritime technology and energy, including T&E, Yara, Siemens, Alstom, CIP, Ballard Power Systems, and Cummins, among others.
ECSA welcomes Parliament's strong support to Ocean Fund and ETS costs' pass-through to operators: European shipowners welcome the strong cross-party support by the plenary of the European Parliament for key provisions under the revised Emission Trading System for shipping. The European Parliament decided its position on the revision of the EU ETS in the run-up to the negotiations with the Council (trilogues). A key element of the Parliament's position is the enforcement of the ‘polluter-pays’ principle, by ensuring the mandatory pass-through of the ETS costs to the commercial operators of the vessels through contractual clauses. ECSA also welcomes the proposal of the Parliament to create a sector-dedicated fund and to earmark 75% of the revenues generated by the shipping allowances to the energy transition of the sector.

Governments
Danish govt to hold co-ownership in future CO2 storage licenses under new political deal: The Danish government has signed a new political agreement with eight parties which implies that it will have a 20% co-ownership in future carbon storage licenses in the North Sea. Danish parties Venstre, Socialistisk Folkeparti, Radikale Venstre, Enhedslisten, Det Konservative Folkeparti, Dansk Folkeparti, Liberal Alliance and Alternativet agreed that the government must have a co-ownership of the CO2 storage permits via the North Sea Fund. The parties also agreed that CO2 storage must be taxed in accordance with the general tax rules. At the same time, the government gets a share of the profits if carbon storage becomes a good business.
Banking on renewable energy, Norway outlines roadmap to turn into 'green industrial giant': The Norwegian government has presented a roadmap for a green industrial boost, setting out measures to bring the country into a low-carbon emissions era through the help of seven industries, which are seen as crucial to curbing emissions and achieving net-zero goals. Within this framework, renewable energy takes centre stage as the key enabler of the transition to a green industry.
Source: Maria Bertzeletou, Breakwave Advisors
The opinions expressed herein are the author's and not necessarily those of The Xinde Marine News.
Please Contact Us at:
media@xindemarine.com
























 Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar 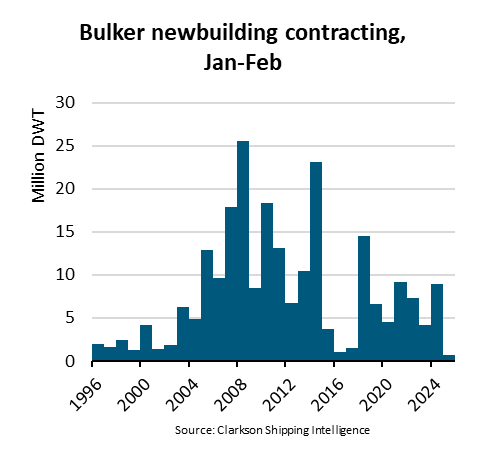 BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi
BIMCO Shipping Number of the Week: Bulker newbuildi  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar  Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar
Ningbo Containerized Freight Index Weekly Commentar